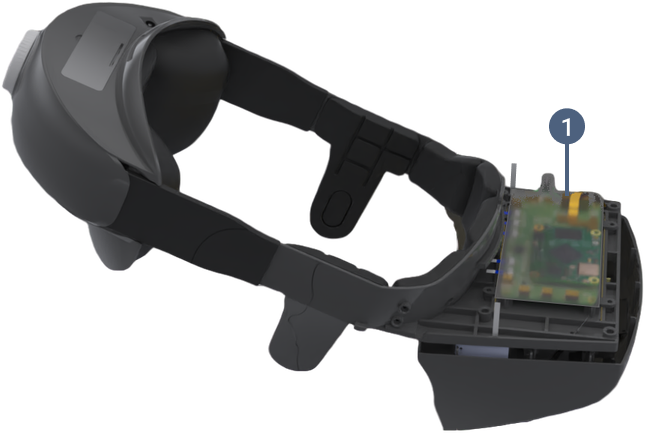
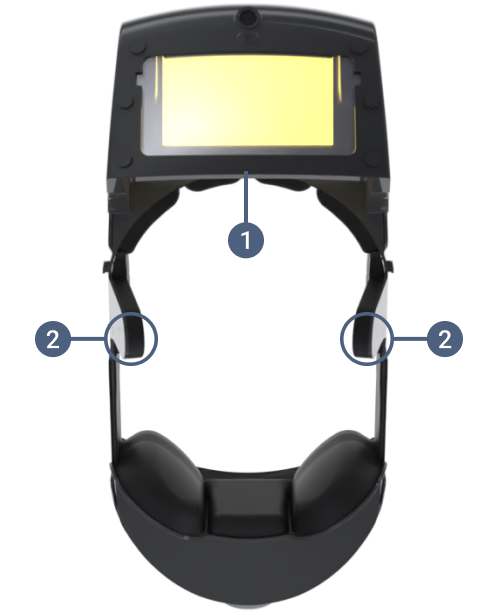
Functionality Details
Overview
The Headset is worn in the same manner as various augmented reality (AR) glasses. It includes
five cameras, two speakers, two microphones, and a hackproof protective coating called a Chassis
Intrusion Detector (CID) which prevents access to the electronics and the combiner. The test is
viewed on a screen called a combiner which includes a Liquid Crystal Shutter (LCS). It is
non-transparent during test taking but becomes transparent at other times.

Cameras
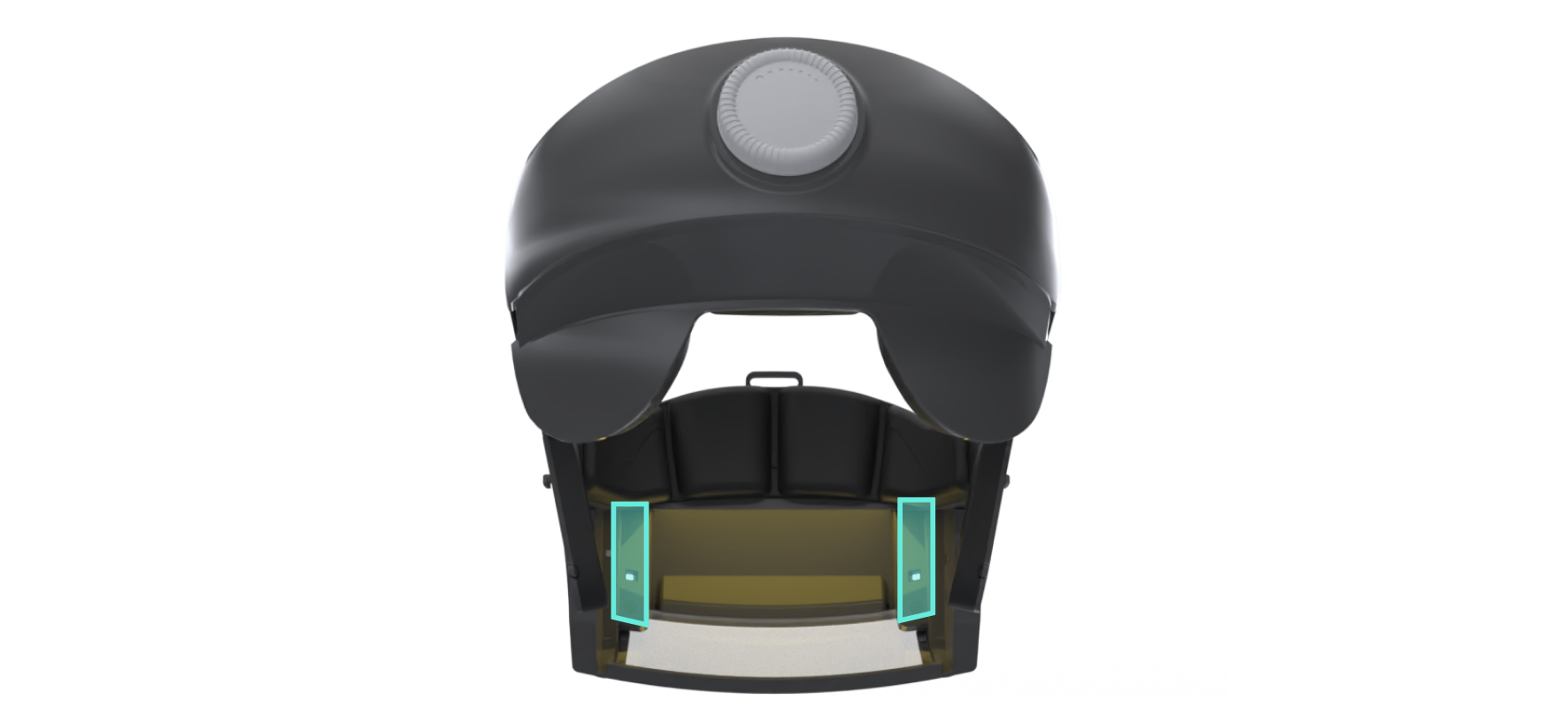

Two Iris Cameras
These cameras image the student’s eyes. They use iris recognition that recognizes, but does not store, the student’s iris biometrics at the beginning of every test. Thereafter, it monitors the location of the eyeballs to detect switching of the glasses to another person or changing in position to enable viewing of the display by a hidden camera.
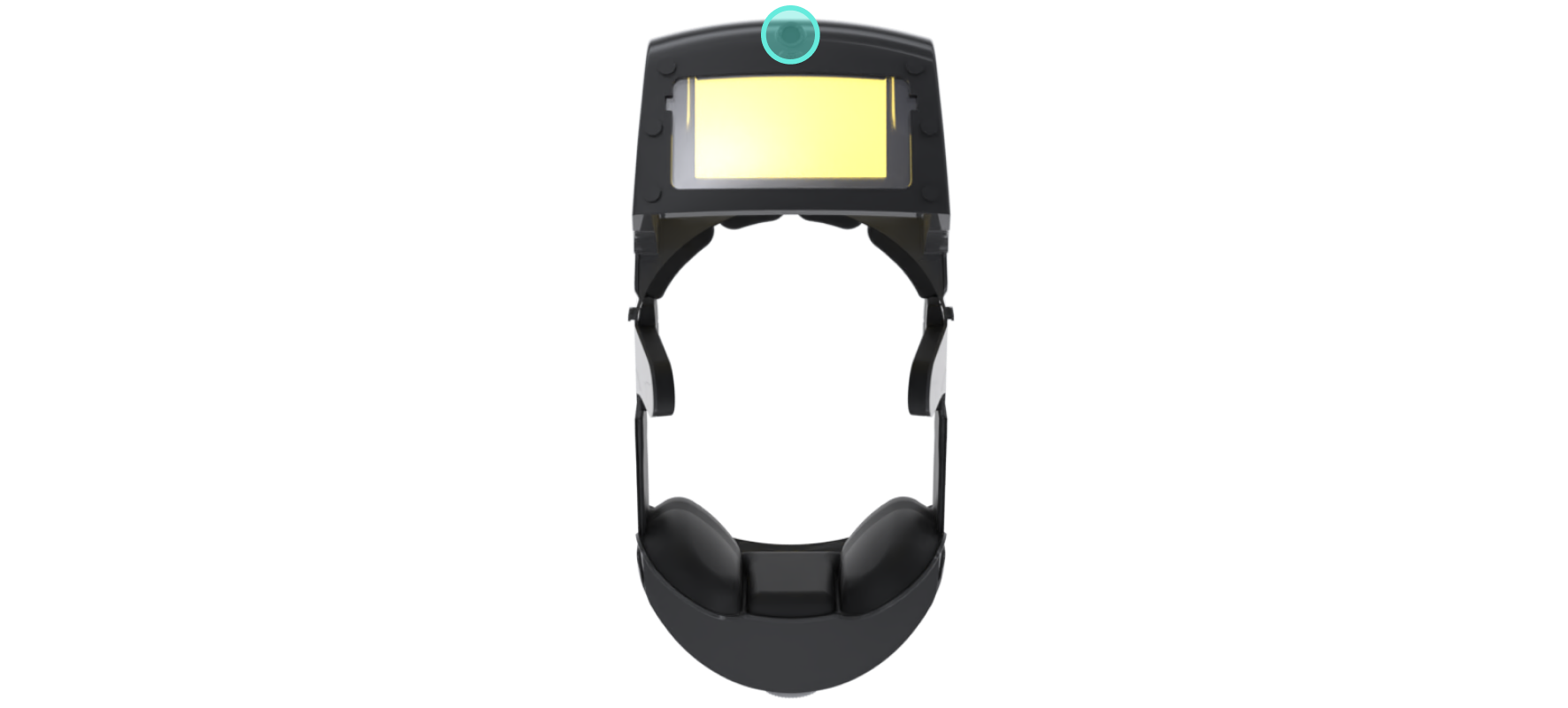

One Forward Looking Camera
This wide-angle camera views what the student can see. It also can record what the
student
is doing with his/her hands thus eliminating the possibility of student-to-3rd party
communication e.g. via typing or writing. The headset image above shows only one forward
looking camera, though an iteration to include two forward-looking cameras for greater
visibility is in development.
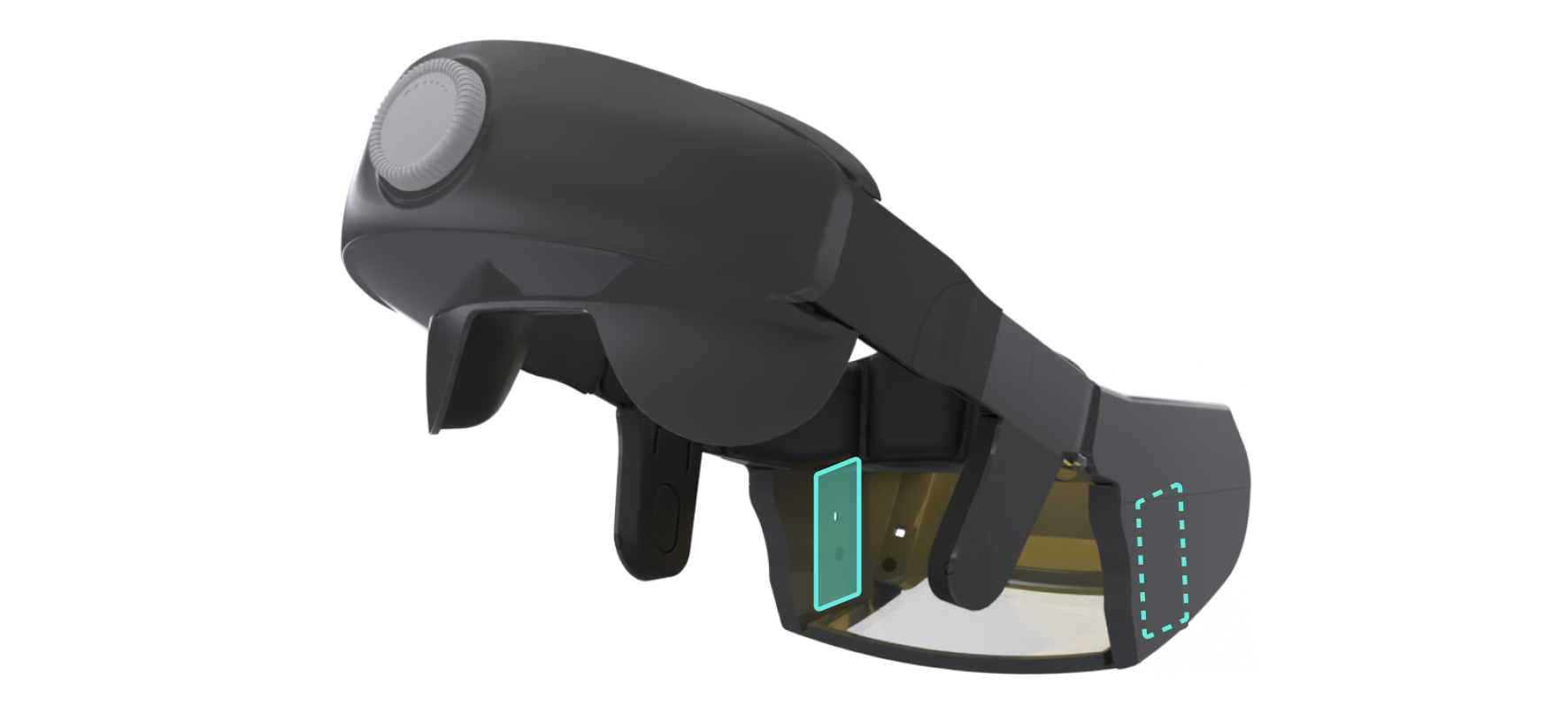
Two Side Looking Cameras
These cameras are positioned on each side of the student’s eyes and view the area
between
the headrest and the face of the test taker. They can detect hidden cameras preventing
communication of test questions to another individual attempting to cheat.
Microphone & Speaker
Contact microphone
To prevent the test-taker from reading the questions and answer choices to a 3rd party,
a
contact microphone is positioned against the head of the test-taker. A contact
microphone is
similar to a physician’s stethoscope.
Contact speaker
The contact microphone rests on the face or cheekbone of the test-taker where it
differentiates
between background sound and the test-taker speaking. A contact speaker periodically
transmits a
sound using bone conduction. If the contact microphone fails to record the speaker
output, then
the microphone is not properly mounted most likely because it has been tampered with,
and the test can be interrupted. If test-taker talking is detected, a warning is
provided
and the test may be terminated.